
Aleph Zero
Latest News
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
- Low fees - Transaction fees are around 0.0003 AZERO
- Fast finalization - Transaction finalization takes around 0.9 seconds
- Private smart contracts - Adaptable functions for automation and programmability
Weaknesses
- Trust: The only major weakness so far is the lack of history of the Aleph Zero blockchain, meaning that over time and under full operation, its shortcomings may be revealed
Basic Information
The public blockchain Aleph Zero stands out for its increased privacy and integration with the Substrate stack. This technology addresses the shortcomings of existing distributed ledger platforms by offering higher speed, scalability, and security. The system is powered by its own algorithm, which uses Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) technology and surpasses the competition in the industry with a practical approach to value transfer and the expandability of smart contracts.
The overall goal of the Aleph Zero project is to enable small and medium-sized businesses to communicate at speeds close to what they would expect with normal internet communication, while leveraging the benefits of decentralization.
The team behind the Aleph Zero blockchain is very extensive and consists of more than 40 members with a diverse range of experience contributing to network development. The team members have several successes behind them, such as the World Finals of the ACM ICPC, winning an international mathematics competition, and receiving the Simons-Berkeley Research Fellowship.
Upgrade to premium
Functioning of the Chain
The Aleph Zero blockchain is powered by the AlephBFT protocol and utilizes a modified version of the Proof of Stake (PoS) methodology in combination with Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG). While the PoS algorithm rotates a set of validators to determine the truth of the blockchain state, DAG serves as an intermediary in creating the Aleph Zero blockchain.
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG)
DAG divides the algorithm's operation into virtual rounds, so that in each round, each node broadcasts exactly one unit, which can be thought of as a message being sent to all other nodes. In addition, each such unit should have "pointers" to a sufficiently large number of units from the previous round broadcast by other nodes. These pointers can be implemented by including hashes of the corresponding units, which allows the unambiguous determination of the "parent units."
Formally, each unit has the following fields:
- Creator - Index and signature of the unit's creator
- Parents - List of hashes of the units
- Data - Additional data to include in the unit
DAG construction Unit:
- Unit structure
- Unit creation Rules
- Protection against network forks
- Disseminating units
Unit Structure
In the AlephBFT implementation, the structure of the DAG is simple. Each unit in the graph contains an array of information, including who created it, what data it carries, and when it was created. Each unit also has a "parent map" that determines who its direct parents were in the previous round. The control hash is a fingerprint of the unit's parent list, and the signature serves as proof that the node created the unit. Parents (units) denote the set of all units to which the unit has edges, and we refer to the hash of the serialized fields of a unit without a signature as a hash (unit).
Unit Creation Rules
Each node maintains a local copy of the DAG structure. If a node wants to add a unit to the DAG, it must ensure that all of the parents of that unit are already in the DAG. If these conditions are met, the node can create a new unit with data from the input stream and send it to all other nodes. After creating a unit, the node must also wait a period of time to prevent the rapid growth of the DAG, which could be problematic for practical reasons, such as bandwidth and node memory limitations.
Protection Against Network Forks
This protocol includes each node in the system creating one unit per round. This is enforced through a reliable broadcast protocol that guarantees that at most one unit is assigned to each creator per round. However, the implementation of this reliable broadcast protocol can be inefficient. To address this issue, AlephBFT also includes a version called QuickAleph, which allows malicious nodes to create multiple unit versions, called forks, for a given round. This makes the protocol more complex, but it is much more efficient in practice because it assumes that most nodes behave honestly, and that forks only occur in exceptional cases. If a fork is detected, the protocol reverts to using the reliable broadcast protocol, which will notify all nodes.
Dissemination
When an honest node accepts a unit, all other honest nodes eventually accept it too. In AlephBFT, several mechanisms ensure that units are disseminated smoothly. The creator broadcasts the unit, nodes broadcast the latest units, and there is also a request-response mechanism that allows nodes to obtain missing units from other nodes.
AlephBFT
The second crucial component of the protocol is Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT). AlephBFT is a system that allows nodes in the network to collaborate and reach a consensus on transactions. Each transaction is represented by a unit that goes through several steps before being processed and added to the network graph. The unit is created by a node and contains information about the transaction. It is then accepted by another node, which validates it and places it in the legal unit storage. Finally, the legal units are passed to a component called the Extender, which processes and adds them to the network.
The BFT consensus model assumes that less than 1/3 of the nodes in the blockchain are malicious, but if 2/3 of the nodes are honest, the BFT blockchain can operate safely and transparently.
For greater security, a rotating committee was introduced, meaning that network validators alternate within a certain time frame. Additional security is ensured by using the element of asynchronicity, meaning that the network will operate smoothly and maintain data correctness even if some of its parts are not functioning. The introduction of asynchronous properties into BFT is a step forward in ensuring maximum security.
AlephBFT consists of:
Creator
- Creates units according to AlephBFT protocol rules
- Waits for a prespecified delay and attempts to create units using the maximum number of parents
- If this is not yet possible, it waits until enough parents are available
- Creator only chooses parents; the rest is filled by runway
- Stops producing new units after creating the last unit
Unit Store in Runway
- Stores only legitimate units and passes them to terminal
- If a fork is detected by a node, all units attached are put on appropriate alert
Terminal
- Receives legitimate units, but may encounter issues preventing them from being added to the DAG
- A unit U might have a "wrong" control hash, triggering a request to the member to download the full list of U's parent hashes to resolve ambiguity
- A unit U might have parents that are not legitimate, so terminal waits for all parents of U to be added to the DAG first
- If terminal does not have a unit for the particular slot in U's parents, it makes a request to Member to retrieve such a unit
Extender
- Receives DAG units from terminal and extends output stream
- Maintains the round for which the next head must be chosen
- Some caching made in implementation to avoid recomputing all votes from scratch
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a mathematical structure composed of nodes (circles) and directed edges (arrows) that point from one node to another. The edges in a DAG are directed, meaning they have a unique direction with one end labeled as the source and the other as the destination.
An important feature of a DAG is that it does not contain cycles, which are sequences of edges that form a loop. This is important because it would cause issues when processing data.
In the case of blockchains, a DAG is used for transactions in the blockchain. Each transaction is represented as a node in the DAG and is connected to other nodes by directed edges, based on how the transactions are linked and dependent on each other. Thanks to this structure, transactions can occur in parallel and independently, increasing the efficiency and speed of data processing in the blockchain.
Development History
2019
- August, the whitepaper was released and Aleph Zero joined the Swiss-Polish Blockchain Association (SPBA)
2021
- April, Aleph Zero acquired the ticker AZERO
- June, Liminal was introduced (Multichain privacy layer for Web 3.0)
- July, the testnet was launched
- October, the public sale took place
- November, Aleph Zero was accepted into the Parity Substrate Builders program
2022
- January, the Ambassador program was launched
- January, the Aleph Zero Smartnet was launched for testing smart contracts
- March, staking was launched on the testnet
- May, bots were deployed on the testnet for simulating real conditions
- June, smart contracts were launched on the testnet
- August, the testnet was opened for community validators (until then it had only operated through the validators of the Aleph Zero foundation)
2023
- January, the testnet was updated
- January, Aleph Zero won the parachain auction on Polkadot
- January, a support program for developers was launched in collaboration with Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- February, the first NFT marketplace on the Aleph Zero blockchain (called ARTZERO) began operating
One interesting bug was found where incorrectly configured infrastructure caused the removal of active storage for four validator nodes on May 2, 2022, effectively deactivating and removing them. The problem was immediately detected by the monitoring system and handed over to the team for emergency resolution. The incident led to the implementation of a stricter code review process and policies that enforce maintenance planning to be more spread out over time to minimize the possibility of similar failures in the future.
An interesting fact during this test was that even without 40% of nodes in the network, it continued to function. The transactions were not finalized because a minimum of 7 validators is needed for finalization, but blocks were still being created (slowing down from 1s to 1.7s per block) and transactions were being accepted.
This demonstrated the asynchronicity of the entire network. The incident also emphasized the importance of decentralization and strengthened the team's conviction to move towards complete decentralization.
Team
Adam Gągol - Co-founder
Adam is a co-founder of the Aleph Zero Foundation and a partner at Cardinal Cryptography. He has a PhD in mathematics with a focus on the application of probabilistic methods in combinatorics. During his doctoral studies, he received the SET project for interdisciplinary research and the SSDNM scholarship for mathematical sciences. Although his main domain is combinatorics, Adam has experience in data science and machine learning applied to neuroscience research. Recently, he has been educating himself in the field of privacy protection in blockchain, zero-knowledge proofs, and secure multi-party computation to create frameworks for private DeFi.
Matthew Niemerg - Board President
Matthew is the Chairman of the Board of the Aleph Zero Foundation and has a PhD in mathematics in the field of numerical algebraic geometry. He is also a Simons-Berkeley Fellow and an IBM Center of Excellence Fellow in High-Performance Computing at Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Since 2014, he has been actively involved in the field of DLT and has provided advice on a number of projects. Matthew specializes in security, consensus models, cryptographic schemes, and applying reasonable business and technological models to DLT projects so that they can operate within clear regulatory frameworks.
Michał Świętek - Co-founder
Michał is a co-founder of the Aleph Zero Foundation and a partner at Cardinal Cryptography. He graduated from Jagiellonian University in Krakow, where he obtained a PhD in pure mathematics for his work in the field of infinite-dimensional geometry of Banach spaces, and a bachelor's degree in computer science. He has applied his impressive skills in various areas, including deep reinforcement learning, machine learning, and neuroscience. In recent years, he has been fully focused on distributed ledger technology, an area that revolutionarily combines mathematics and computer science.
Antoni Żółciak Co- founder
Antoni is a co-founder of the Aleph Zero Foundation and a managing partner at Cardinal Cryptography. He has over a decade of experience in technological marketing and has worked on various projects for companies such as ING, Samsung, Sony, Olympus, and Nikon. Before joining In'saneLab, he worked as an inbound marketer for Brand24 and Codewise, the second-fastest-growing company in Europe according to The Financial Times. Antoni is also a member of the American Marketing Association. In recent years, Antoni has been actively involved in the Web 3.0 field and has worked as a consultant for AngelBlock.
Cardinal Cryptography, along with the Aleph Zero Foundation, offers research, development, and marketing support for anyone looking to deploy this network. This means that companies and organizations can work with these entities to create their own applications that utilize the distributed ledger as a foundational element.
The Cardinal Cryptography team comprises over 40 talented individuals who are actively involved in Web 3.0 development. The team members have achieved success in various fields, including participation in the world finals of ACM ICPC, winning first place in an international mathematics competition, and obtaining a Simons-Berkeley Research Fellowship.
Experience is a key component of their success, and they pride themselves on their expertise in cryptography, security, computer science, and mathematics.
Governance
The native coin of the Aleph Zero blockchain is called AZERO, and its uses are:
- Staking
- Voting
- Paying transaction fees
Any holder of AZERO coin can propose a change to the protocol. Submitting a proposal costs 100 AZERO coins, but note that if it is not approved, you will lose these coins. All AZERO coin holders can vote on proposals. If you do not vote personally, your votes will go to your validator, who will vote on your behalf.
The steps that the Aleph Zero Foundation has taken on the road to decentralization are:
- In the first step, the foundation introduced nodes that ensured transaction integrity, but community members could not become validators
- In the second step, a nomination mechanism was introduced that allowed users to delegate their tokens to foundation nodes, and inflation was introduced to motivate users
- The third step involved the introduction of external validator committees, with the Aleph Zero Foundation retaining a majority
- In the fourth step, the foundation continued to open the committee to external validators until the community controlled it, and foundation nodes charged higher commission fees to motivate nominators to nominate community nodes
- In the fifth step, the Aleph Zero Foundation will become a decentralized network in terms of validation, with AZERO being the tool by which you will decide on the future of the ecosystem in voting
We are currently in the fourth step, and after the mainnet is launched, the entire plan for a decentralized network will slowly become a reality. Currently, 71% of the circulating supply (332,358,000) is staked with 125 validators.
Revenue & Tokenomics
Aleph Zero’s revenue to date has come from the pre-sale of the AZERO coin, but in the future, the revenue will be generated from fees for using the blockchain. AZERO is a relatively new cryptocurrency that was launched in 2021. The total supply is set at 300 million coins, with an annual inflation rate of 30 million coins. The initial offering was 160 million coins. Currently, there is no mechanism for burning coins, but this may change with the development of the ecosystem.
The distribution of the AZERO coin

- 23% - Aleph Zero foundation (allocated to the foundation, this will be spent on research and development, marketing, operations, as well as ecosystem incentives and other operational expenses)
- 18.33% - ICO (1 AZERO = 0.01 USD)
- 16.66% - Contributors (1 AZERO = 0.04 USD)
- 16.66% - Seed round (1 AZERO = 0.057 USD)
- 10% - Team (Out of the team allocation, 80% of the coins will be locked for one year and vested over four years.)
- 10% - Public sale
- 5% - Early Community round (1 AZREO = 0.07 USD)
Vesting schedule

The table provides information on the current distribution of AZERO. As can be seen, all AZERO have been unlocked and are available to all investors. The remaining coins will be allocated to the team and the foundation. The inflation rate is another important factor that affects the value of AZERO. Since the annual inflation rate is set at 10%, 30 million new AZERO coins will be created each year, which may impact its price.
The total number of staked coins by validators is 71 % of the total number of 332 million coins.
The current inflation rate is 9% (as of May 30, 2023).
The Uniqueness of the Chain
Liminal: This is a privacy solution that is designed to offer additional measures for securing and protecting privacy while also serving as a portal for other blockchains. Liminal uses a unique combination of zero-knowledge proofs (ZK-SNARK) and secure multiparty computation (sMPC) to ensure the security and anonymity of client data. ZK-SNARKs are used to prove the correctness of the update of a private state that can be verified using the blockchain, while sMPC is used to implement the concept of a global private state, such as in a decentralized exchange. The hybrid arrangement of Liminal provides additional measures for securing and protecting the privacy of client data.
Hybrid consensus protocol: Aleph Zero has developed a new consensus protocol called AlephBFT, which ensures maximum theoretical security. The protocol can tolerate up to 33% malicious committee members without affecting the verification process. Each transaction is confirmed once 67% of members agree with it. Asynchrony is a key feature of the Aleph Zero network, which does not rely on any time assumptions and ensures that all honest transactions are confirmed, even during complete network asynchrony. Additionally, the Aleph Zero network aims to be decentralized and leaderless, with no single node controlling the creation of the overall order of units at any stage of the process. The result is a distributed resilience of the network against denial-of-service attacks and the easy recovery of the protocol after a network split.
Cloud storage: This is a decentralized solution for file storage, supported by the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS). It offers a secure, private, and reliable platform for storing and sharing files.
Smart contracts: Aleph Zero focuses on creating smart contracts that are fast, secure, and include complete Turing functions. These contracts are designed to be adaptable and scalable for high-performance computing applications. This opens up new opportunities for systems with complex machine learning components and other automated services that can be applied on a large scale.
Common: This is one of the first products built on the Aleph Zero platform, which utilizes its scalable architecture and fast transaction finalization. Specifically, it is a DEX and a universal wallet that eliminates problems with front-running.
Dynamic Fee: This solution works as a tool for organizing the network during times of high traffic. In addition, it offers fees that correspond to the level of user involvement. The feature of giving tips to users also helps prioritize transactions during network congestion.
How the Network is Secured
The security of the entire blockchain is taken care of by 125 validators (as of March 25, 2023), with 8,016 active nominators staking with them.
The defensive mechanisms that protect the Aleph Zero blockchain from malicious users include the slashing mechanism, which financially penalizes users for disrupting the network. However, the Aleph Zero blockchain team has decided not to use an automatic slashing mechanism. Instead, as a means of combating harmful actors, the team may use a tool to freeze the assets of suspicious users.
Freezing assets would involve temporarily suspending the capital staked by the suspicious user. An investigation would first be conducted to determine whether an internal error occurred, or whether the user had malicious intent. This individualized approach to each case is much fairer than indiscriminate slashing. After the investigation, the team could either enforce fund slashing or release the funds back to the owner if it turns out that the suspect is innocent and the error was caused, for example, by a code error. Initially, the decision will be made by the Aleph Zero foundation, but as adoption grows, decentralized management will make the decisions.
In the entire history of the network since the launch of testnet and mainnet, no cases of dishonest behavior by validators have been recorded. This suggests that the network could be secure and users are mostly adhering to the rules and ethics.
Bug bounty program
Currently (as of March 25, 2023), there is no active bug bounty program for the Aleph Zero blockchain.
Aleph Zero has previously worked with Immunefi on a bug bounty program that focuses on identifying vulnerabilities that could impede the deployment of smart contracts. The program was designed with the help of Immunefi to reward developers who helped identify weaknesses that could impede the development of the Aleph Zero company. These invaluable insights allowed Aleph Zero to build a more secure network and protect both the Aleph Zero blockchain and its user base.
Nodes
In the Aleph Zero blockchain, a node can be used in two ways:
- Archiver: Only stores blocks and can respond to queries about the state of the network
- Validator: Actively participates in consensus and is responsible for creating new blocks (validator nodes receive rewards for block creation)
OWN NODE (validator)
To run your own node on the Aleph Zero blockchain, you will need a minimum of 25,000 AZERO coins and sufficient hardware.
Minimum setup:
- CPU - 4 cores x86_64
- RAM - 16 GB
- SSD - 1 TB
- Network - 25 Mb/s ( 24/7 online)
Cloud minimum setup:
- AWS - c5.large
- GCP - c2-standard-4
- Azure - F4s (+ additional persistent storage)
Recommended setup:
- CPU - 8 cores x86_64
- RAM - 32 GB
- SSD - 2 TB
- Network - 100 Mb/s (24/7 online)
Cloud recommended setup:
- AWS - c5.xlarge
- GCP - c2-standard-8
- Azure - F8s (+ additional persistent storage)
These videos will help you with the overall setup and launch of your node
Validating on Aleph Zero - Part I - Node Setup
Validating on Aleph Zero - Part II - Setting your Node Identity
Validating on Aleph Zero - Part III - Making your Node Validate
You can find more information here.
Benefits of a validator:
- Earn new AZERO coins
- Contribute to the security of the blockchain
- Help decentralizing the network
NOMINATOR
There are two types of nominators in the Aleph Zero blockchain:
- Direct nomination
- Pooled nomination
Direct nomination:
The direct nomination process in the Aleph Zero blockchain is relatively simple and requires you to own at least 2,000 AZERO coins. Potential nominators can easily stake their coins to a chosen validator. However, it is important to keep in mind that the minimum amount of coins required for direct nomination may increase in the future to improve the network's security and prevent possible centralization.
Pooled nomination:
This method allows multiple users to act as one nominator and create a joint stake. There is no need for trust between users, so there is no loss of security. Nomination pools are open to all holders who own at least 10 AZERO, making this feature more accessible to more users. Creating a nomination pool is both quick and easy, as all you have to do is find other users who want to create a stake together and create a pool. All participants can then contribute to the nomination decision-making and stake management.
Benefits of a nominator:
- No hardware needed
- Rewards from validator
- Supports decentralization of the blockchain
- Contributes to the security of the blockchain
Road Map
Aleph Zero has a divided Road Map into certain steps they want to achieve, but which are not directly tied to specific dates. This is usually announced before final deployment on the mainnet.
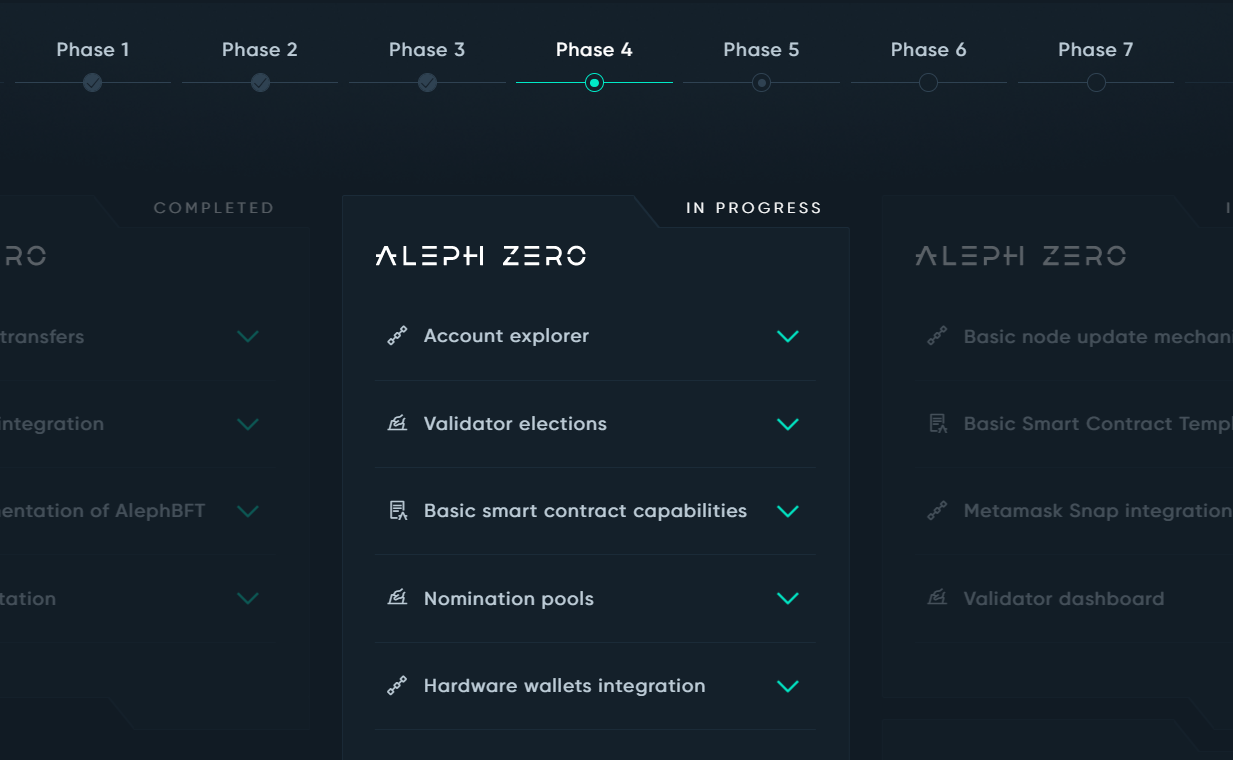



Q1/Q2 2023 - Working on:
- Account explorer - Improving the dashboard for more detailed information display
- Validator elections - Providing fairer distribution of validators for network validation
- Basic smart contracts (SC) capabilities and templates - Deploying SCs on the Aleph Zero mainnet and interacting with wallets
- Nomination pools - Improving the interface for creating pools
- Hardware wallet integrations - Integrating Ledger and Signer hardware wallets into the Aleph Zero blockchain
- MetaMask snap integration - Integrating the MetaMask software wallet into the Aleph Zero blockchain
- Validator dashboard - Modifying the dashboard to display more information about validators
- Liminal - Integrating ZK-Snarks for greater privacy of dApps on the Aleph Zero blockchain
By launching smart contracts on the Aleph Zero mainnet, this blockchain network becomes fully operational and ready for mass adoption. Smart contracts are programmable contracts that allow for the automatic execution of conditions and restrictions, simplifying and accelerating the entire process. This step will also bring the possibility to use dApps based on smart contracts.
Ecosystem
The full launch of smart contracts on the Aleph Zero mainnet was deployed on March 29, 2023, and it was be a key milestone for the entire ecosystem. This moment marked the official beginning of the development of the DeFi world on this platform, allowing users to take advantage of a wide range of decentralized financial services, such as loans, staking, yield farming, and much more. After the smart contracts launch, support for an extensive range of tokens and the creation of new tokens was introduced, opening the way for further development of DeFi on the Azero blockchain.
Here, you can find the ecosystem on the Aleph Zero blockchain.
Currently, the native DEX, PanoramaSwap, is already in operation. This DEX was built on the Aleph Zero blockchain and it allows users to exchange various cryptocurrencies and tokens without having to trust a third party. PanoramaSwap has very low fees and fast transaction times, making it an attractive choice for users who want to trade cryptocurrencies on a decentralized exchange.
Grants program
Aleph Zero is part of the Parity Substrate Builders program. which is an initiative by Parity, the company behind the Polkadot blockchain. This program provides funding and support to developers who are working on developing new blockchain solutions for the Web 3.0 ecosystem.
The Aleph Zero ecosystem has received significant support in the form of grants, operational advice, marketing, and business strategies through their program for several months. This allows Aleph Zero to obtain the necessary financial support and access to the experience and resources of Parity, which is crucial for the development of new solutions.
Community
The main communication channel during development is Discord. All errors and fixes during testing are discussed and corrected on the platform.
The Discord community around the Aleph Zero project is very large and active. Newcomers are warmly welcomed and there is a high level of interaction among existing community members. Everyone has a common goal - the successful launch and development of the project.
It is evident that the Aleph Zero project has captured the attention of many people who want to contribute to its successful launch and the growth of its ecosystem. Collaboration between developers and the community through Discord enables the project to quickly respond to changes while ensuring high quality of the final product.
Apart from a few educational videos on the validation and inflation of the AZERO coin, the Aleph Zero YouTube channel does not yet have much content. However, it does provide a great start for new users who want to better understand how inflation works. The YouTube channel could be further developed with additional educational videos, such as how to get started with using the platform and developing dApps. By creating more content on the YouTube channel, Aleph Zero can ensure that users have access to the necessary information and can more easily learn how to use and benefit from the ecosystem. In this way, the platform would be more likely to attract new users and support community growth.
Partners
Where to Buy
If you want to buy on a DEX (Decentralized Exchange), only one is currently functioning:
When buying on a CEX (Centralized Exchange), always check if it supports AZERO. The AZERO coin is the 144th largest cryptocurrency, but it is currently in its early stages where not all CEXs support it yet.
Here are three examples:
Supported Wallets
Nova Wallet - SW (software wallet)
SubWallet - SW (software wallet)
Analyst Opinion
It is true that many projects in the crypto world have promised similar improvements as the Aleph Zero project. However, many of these projects have ultimately failed to fully deliver on their promises and bring the desired level of innovation and performance. One of the main reasons why the Aleph Zero project has been surrounded by such hype is the fact that it is at the beginning of its development, which allows it to more easily adapt to new technologies and improvements.
Many people compare Aleph Zero to the Solana blockchain, which has experienced a huge surge in popularity of late. However, Solana also struggles with occasional outages and issues with smooth blockchain operation, which may be a result of its rapid growth and increased workload. On the other hand, the Aleph Zero project is striving to address these issues in its early stages of development, so that it can be launched smoothly and offer stable, fast operation that will not be disrupted by any technical difficulties.
With its unique technology and ability to provide speed and stability in blockchain operation, the Aleph Zero project could provide many advantages for users and investors in the cryptocurrency space. Hopefully, the Aleph Zero project will be successful in achieving its goals and serve as inspiration for more innovative projects in the crypto world.
Previous

Next





.webp)

.png)






.png)



.png)


.png)

.png)


.webp)

.png)


.png)


.png)




.png)
.png)
.png)


Social Networks
https://discord.com/invite/alephzero
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.05156.pdf
https://docs.alephzero.org/aleph-zero/
https://alephzero.org/
https://beincrypto.com/learn/aleph-zero/
https://medium.com/aleph-zero-foundation