
Polygon
Latest News
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
- Fast transactions: Polygon can handle up to 65,000 transactions per second
- Cheap transactions: a transaction on the Polygon Chain costs around 0.01 USD
- Scalability: Polygon is built to scale as transaction volume increases
- Security: shares security with the Ethereum blockchain
Weaknesses
- Ethereum 2.0: Polygon may not be needed after the Ethereum blockchain transitions to PoS
- Competition: strong competition among multi-chain projects
Basic Information
Polygon is the 2nd layer (L2) of the Ethereum blockchain, operating on the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus.
Polygon, formerly known as the Matic Network, is aiming to scale the blockchain by providing tools that will speed up and reduce the cost of blockchain transactions. It is supporting the development of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) and is assisting the Ethereum blockchain with scaling up, becoming faster, and more secure.
Polygon is a solution for scaling public blockchains that supports all EVMs, along with faster and cheaper transactions.
$MATIC remained the native coin after the renaming of Matic Network to Polygon.
Upgrade to premium
Functioning of the Chain
Polygon consists of side chains, which are compatible with the Ethereum blockchain:
- Standalone chains: standalone chains are compatible with the Ethereum blockchain and handle their own security (with their own validators)

- Secured chains: these chains rely on the security of the larger blockchain (Ethereum). This eliminates the need for them to operate their own validators

The side chains are further divided into layers as follows:

- Execution layer: this layer handles the execution of transactions and smart contracts (EVM)
- Polygon network layer: each chain is programmed for a particular purpose – they utilize their own consensus mechanism for creating blocks
- Security layer: specifically, this layer focuses on validators. It does not need to be implemented on every chain connected to Polygon, and is responsible for sharing security across the Ethereum and Polygon blockchains
- Ethereum layer: in this layer, smart contracts are used to communicate between the Ethereum and Polygon blockchains, finalize transactions, and manage coin staking
Polygon operates on the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus.
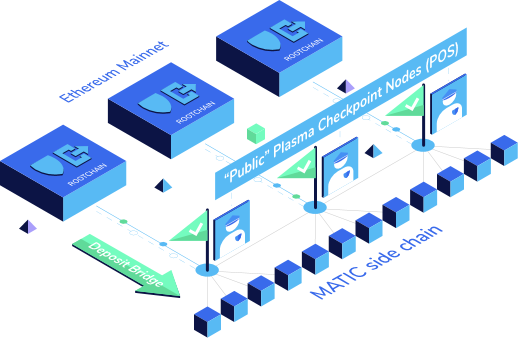
Polygon’s PoS is divided into 3 layers:
- Smart contract staking on Ethereum blockchain: this consists of a set of smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain that manage coin staking for validators, delegations, validator shares, and a status of the side chain.
- Heimdall (PoS layer): Essentially, this is the PoS node software used by validators, which works with smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain and provides PoS consensus on the Polygon blockchain. Heimdall is based on the Tendermint consensus engine, with modifications to the signature scheme and data structures. As part of the Polygon blockchain PoS architecture, Heimdall is responsible for verifying blocks, selecting validators for block creation, and checking blocks on Ethereum side chains. It is also responsible for aggregating the blocks produced by Boron into a Merkle tree, and periodically releasing the Merkle root to the Ethereum blockchain root.
- Bor (Block producer layer): this fills blocks with transactions and is compatible with the EVM
Side chains: there may be additional chains that operate on the Polygon layer, allowing multiple transactions to be merged into a single transaction. To create blocks, Polygon uses plasma chains, which are sent to the main blockchain for final confirmation.
Tendermint: the toolkit for creating a blockchain that makes everything more efficient and easier to use.
Polygon SDK: this is another toolkit for developing blockchain. The purpose of this package is to meet the needs of developers on the Polygon blockchain for emerging chains. As a "building block," it facilitates the development and connection of new chains. New tools are currently being added to this package while it is still in development.
Due to EVM compatibility, Polygon's side chains are designed to speed up the Ethereum blockchain and make it a fast and friendly place for all users. The Polygon blockchain offers cheap, rapid transactions until a large number of users arrive. When this occurs, the entire Polygon blockchain slows down considerably and transactions become more expensive.
The Polygon blockchain should be able to handle the surge, but for now, it is a work in progress. In order to facilitate the implementation of new side chains, a variety of developer toolkits are being developed. At present, their solution is insufficient in comparison with competitors such as Cosmos and its Cosmos Hub, which handles multi-chains in a slightly different manner, and more effectively.
The crypto world is fast-paced, and things can move forward in a matter of months or years. There is a large army of dedicated developers working behind the scenes at Polygon to ensure its smooth operation in the future.
Development History
2017
- Matic Network was launched
2019
- An IEO on Binance was launched in April, raising a total of five million USD
2021
- Matic Network was renamed Polygon in February
- Polygon Edge and Polygon Studios were launched in June
- Polygon Avail (Optimistic rollup) was launched in July
- ZkEVM (Zero-knowledge) scaling solution was presented in July and introduced in August followed by Polygon Nightfall (August), Polygon Miden (November) and Polygon Zero (December)
- Polygon acquired Hermez Network (now Polygon Hermez) for 250 million USD in August
- The MIR blockchain was purchased by Polygon in December for 250 million MATIC coins (approximately 400 million USD at the time)
2022
- The Polygon Foundation sold MATIC coins to investment firms for 450 million USD in February
- Donald Trump released his own NFT series on the Polygon chain in December, which sold out within one day
Polygon was hacked in December 2021 and approximately 801,000 $MATIC were lost (worth roughly 1.7 million USD at the time). There was a fundamental flaw in the smart contract on the Polygon blockchain, with 9 billion locked coins (20.2 billion USD at the time). What is interesting about this hack is that the team behind Polygon received a notification (on December 3) from two white hackers who identified the flaw in the code. Before the bug could be fixed (December 5) and shared between nodes, another hacker most likely exploited the bug and stole the coins (December 4). Following the incident, the bug was fixed, and the Polygon blockchain team assured users that the security of the entire blockchain had been enhanced. A bug bounty program awarded 3.46 million USD to the white hackers who reported the bug.
Team

A team of four software engineers, Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, Anurag Arjun and Mihailo Bjelic, founded Polygon blockchain (Matic) in 2017.

Jaynti Kanani (CEO): full-stack developer and blockchain engineer who has worked on blockchain projects such as Web 3.0, Plasma and WalletConnect
Sandeep Nailwal (COO): blockchain programmer and entrepreneur who founded blockchain consulting company, Scope Weaver
Anurag Arjun (CPO): previously worked for SNL Financial, Dexter Consultancy and Cognizant Technologies as a product manager
Mihailo Bjelic (Co-Founder): A graduate of the University of Belgrade with a degree in information systems
Governance
The Polygon blockchain’s primary coin is $MATIC.
Usage:
- Transaction fees
- Rewards for validators
- Staking
The governance system is still under development and everything is therefore currently handled by PolygonDAO with PolygonID.
PolygonDAO: Represents the Polygon blockchain ecosystem and distributes grants to new projects. As of now, this organization is run by the Polygon chain team, but in the future, it intends to decentralize its functions in order to establish a neutral party that will support the development of the ecosystem as a whole.

PolygonID: A tool that is designed to contribute to a more decentralized PolygonDAO. It confirms identity with the help of zero-knowledge proofs, and provides access to PolygonDAO governance via governance tokens. These tokens are issued in accordance with the identification of a person who is interested in participating in the governance of the DAO (1 token per person). Personal information is encrypted and anonymous.
Governance module:
As part of Heimdall's governance module, parameter changes are synchronized throughout the network. Through this module, users can submit change proposals and vote on them using their coins. Votes are counted by each validator, who updates their nodes with the new information once the defined voting parameters have been met.
Current voting parameters (expressed in $MATIC):
- Quorum: 33.4 %
- Threshold: 50 %
- Veto: 33.4 %
Here is a list of parameters that can be changed using the Heimdall governance module.
Over 3.5 billion $MATIC have been locked in with Polygon's 100 blockchain validators (as of January 2023).
It does not appear to be a particularly decentralized model at this moment having only 100 validators, but Polygon is aware of this issue and plans to implement more validators in the future to ensure blockchain security.
Revenue & Tokenomics
$MATIC was offered in 2019 as an IEO on Binance.

The distribution of $MATIC is as follows:
- 23.33 % is allocated to the ecosystem
- 21.86 % is allocated to the Polygon Foundation
- 19.00 % is allocated to Binance for IEO
- 16.00 % is allocated to the development team
- 12.00 % is allocated to staking rewards
- 4.00 % is allocated to consultants
- 3.80 % is allocated to private investors
Using the Ethereum blockchain model, a portion of the transaction fees is burned. You can view how many MATIC coins have already been burned at here.
The inflation rate of $MATIC reduces by 0.27 % per year through the burning of part of the transaction fees.
Currently (January 2023), it is approximately 13 % to 15 % per year.
The maximum supply of $MATIC in circulation will be 10 billion coins.
As of 19th December 2022, there are 8,955,469,069 MATIC coins in circulation.
The last $MATIC is expected to be minted in April 2025.

Polygon has received several rounds of funding:
- 165,000 USD was raised in the seed round of 2019 at a coin price of 0.00079 USD
- 440,000 USD was raised by early adopters in 2019 at a coin price of 0.0026 USD
- During Binance's 2019 IEO, 5 million USD was raised at a coin price of 0.0026 USD
- Another round of funding for large companies took place in 2022, raising 450 million USD
The Uniqueness of the Chain
The polygon blockchain attempts to solve scalability and usability issues without compromising decentralization, and by leveraging the existing developer community. It aims to improve existing platforms by providing scalability and a user-friendly environment for dApps.
Scalability: fast, inexpensive and secure transactions on Polygon’s side chains with finalization achieved on the main Ethereum blockchain as the first compatible (L1) base chain.
High bandwidth: in an internal testnet, it was demonstrated that up to 10,000 transactions per second could be processed on a single side chain. As more side chains become involved, the ability to scale becomes more efficient and the number of transactions increases.
User experience: for developers coming from the Ethereum blockchain, EVM support is a significant advantage.
Security: operators of the Polygon blockchain utilize the PoS consensus model through their own staking. Ethereum is responsible for finalizing the blocks.
How the Network is Secured
The Polygon blockchain is secured by 100 validators who compose the blocks, but their finalization is accomplished on the Ethereum blockchain. The Polygon blockchain requires fewer validators to maintain the same level of security as the Ethereum blockchain, due to this shared security.

Heimdall layer:
A validator is created on the Heimdall layer for every few blocks on the Bor layer. This:
- Validates all blocks starting from the last control block
- Creates a Merkle tree based on the block hashes
- Transfers the Merkle tree root to the main blockchain
Polygon's blockchain security is decentralized through validators overseen by delegates. Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus does not require as much computational power as Proof of Work (PoW), but even this small amount of power must be utilized somewhere. In most cases, these servers are leased from Google Cloud Computing Services or Amazon Web Services. The majority of the network's computational power is produced by these services. This entire Polygon blockchain will be affected if these cloud services are e.g. forced to shut down by government authorities in the future.
Nodes
Polygon Chain Validator
To become a Polygon blockchain validator, you must have at least 1,000 MATIC coins in staking, and some computing power.
Minimum system requirements:
- 32 GB RAM
- 8-core CPU
- 2.5 TB SSD
Recommended system requirements:
- 64 GB RAM
- 16-core CPU
- 5 TB SSD
- Internet speed 1 Gbit/s
Here, you can find the settings for your client.
Once you have installed the client, you can stake your $MATIC on the Ethereum network.
In the case of an available slot, the validator is selected immediately for validation. In the absence of a slot, you must wait for the next selection. The more coins you have in the stake (owned or delegated), the greater your chance of being selected.
Validator benefits:
- Earns rewards that are partially distributed to delegates
- Participates directly in the running of the network
Polygon chain delegator
The delegators are holders of $MATIC coins who do not wish to, or cannot operate their own node. Instead, they delegate their coins to a particular validator node, thereby securing the network.
Be aware of the nine-day lockout period when unstaking your coins from a validator as for that period of time you will not be able to manipulate with your coins.
You can select a validator for staking your coins here.
A percentage of the validators' commission is set by the validators. Delegates are able to view the commissions of each validator. This allows them to determine reward distribution and what rate of return they receive from staking their coins.
Delegate benefits:
- Indirect participation in the operation of the network
- Hardware and other extra costs are not required
- Contribution to the network's security
Road Map

Polygon has several scaling solutions in development:
Polygon zkEVM (test phase): Zk-Rollup is a layer-2 tool that addresses scalability by processing bulk transfers bundled into a single transaction. Zero-Knowledge (ZK) proof technology is used to present and publicly record the validiity and correctness of rolled transfers processed on the Ethereum blockchain. By storing only the proof and compressed transfer data, the efficiency and bandwidth of the blockchain are increased.
Polygon Avail (in development): Avail is a blockchain focused on data availability, and whose purpose is to trigger and record blockchain transactions. It facilitates the availability of data in a block to be proven without having to download the entire block. As a result, this takes scaling to a level that is not possible with traditional blockchains.
Polygon NightFall (test phase): A major objective of NightFall is to reduce the cost of converting ERC-20, ERC-721, and ERC-1155 tokens. It uses Optimistic Rollup to reduce transaction fees and ZK to ensure privacy. The Optimistic Rollup contracts are deployed on the Ethereum blockchain. There is no need to rely on a third party outside the blockchain to perform a private transfer, as all information is available to the users themselves.
Polygon Miden (in development): Miden relies on ZK technology to "roll up" thousands of layer-2 transactions into a single transaction on the Ethereum blockchain, thereby increasing bandwidth and reducing transaction fees. The heart of Polygon Miden is the Miden VM, a Turing-complete STARK-based virtual machine that offers a high level of security and supports advanced functions that are not available on Ethereum blockchain.
Polygon Zero (in development): Zero is a layer-2 scaling solution for the Ethereum blockchain. In comparison with other solutions, Zero introduces Plonky2, which generates ZK proofs faster than any other existing technology. Plonky2 supports efficient recursive proof generation, enabling it to scale horizontally. Thus, the protocol's bandwidth is not limited by the weakest nodes, but by the total available computing power.
All of these tools are still in the development or testing phase. None of them have been implemented on mainnet yet.
Several milestones will be reached in the near future, such as the launch of multiple side chains, which could significantly improve the scaling of the Polygon and Ethereum blockchains (so far, only one has been launched).
If we compare the Polygon and Cosmos chains, we can see that in contrast with Polygon, Cosmos already has multiple blockchains that can be connected to the main blockchain Cosmos Hub.
Ecosystem
There are plenty of DeFi projects on the Polygon blockchain due to EVM compatibility and fast, cheap transactions.
The largest DeFi projects on the Polygon blockchain:
- AAVE – Lending/borrowing
- Quickyswap – DEX
- Balancer – DEX
By 21st December 2022, there were more than 150 active DeFi protocols on the Polygon blockchain, with a combined TVL of 1.38 billion USD.
Polygon has its own investment fund for developers, called the Polygon Ecosystem Fund.
Individual developers may apply to this fund for support for their projects.
The Polygon Blockchain Development Fund is funded by various companies:
- Wintermute: a digital asset company that invested 20 million USD in 2021
- Seven Seven Six (776): a venture capital company that invested 200 million USD in 2021
- Outlier Ventures: contributes to the development of blockchain. Their joint effort in 2022 led to a backing program that selects new projects and provides various forms of development support.
Community
The Polygon Discord has a very welcoming community. There is always someone available to answer your questions, and they hold regular AMA (Ask Me Anything) sessions, during which you can ask the developers about a specific project or update.
The Twitter account has been very active in releasing news about the Polygon blockchain and its partners.
They also host a variety of podcasts on YouTube, addressing the Polygon blockchain and its development. In addition to this, there are numerous educational videos available about various improvements on the blockchain.
Partners
Where to Buy
$MATIC can be bought on almost all centralized exchanges (CEXs).
When buying on a decentralized exchange (DEX), it is best to use those on the Polygon blockchain:
When buying on a CEX, you are not limited to any one exchange. $MATIC is the tenth largest cryptocurrency and is therefore supported by almost all exchanges.
For example:
Supported Wallets
Ledger Nano X – the most widely used hardware wallet (HW) on the market. When paired with your software wallet (SW), you get more security for your cryptocurrencies
TrustWallet – SW wallet
MetaMask – SW wallet
Analyst Opinion
Polygon is attempting to make Ethereum a true multi-chain that will benefit from all types of scalability at layer 2, not only the initial implementation of the previous Matic Network.
In 2021, Polygon showed its limitations when fully utilized. The speed of processing and finalizing transactions was miles away from the plans of the Polygon development team. The only what could be delivered at that time was low transaction fees, but these came at the expense of long wait times or a lack of bandwidth. However, the team has done an excellent marketing job, managing to erase the memory of that period.
In order to make Ethereum a true "Internet of Blockchains," Polygon plans to develop further scaling infrastructure and a full-fledged multi-chain. Currently, it is running only one side chain, which is not sufficient to solve any problems. Thanks to the members of the Ethereum blockchain community who have become Polygon blockchain advisors, Polygon has greater support among Ethereum blockchain developers.
Polygon's plan is ambitious and it has the necessary technology to help it achieve its goals. Despite this, it remains to be seen whether or not the Ethereum blockchain will require the scaling of the Polygon blockchain once PoS has been deployed. The Polygon blockchain may even separate from the Ethereum blockchain and go its own way. However, this is unlikely at this point in time.
Previous

Next






.webp)

.png)






.png)



.png)


.png)

.png)


.webp)


.png)


.png)


.png)




.png)
.png)
.png)

Social Networks
Lightpaper Polygon
Github
101Blockchains
Cointelegraph
Gemini
Wiki Polygon
WorldCoin
Coingecko
Unblock
BlockDaemon
Coin98
Twitter