.png)
Ethereum
Latest News
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
- Operation of smart contracts and dApps – Ethereum blockchain is the cradle of smart contracts and dApps
- No outages – Ethereum has never experienced a network outage during its entire history. Every update is thoroughly tested on testnet before being seamlessly implemented on the mainnet
- ERC–20 standard – as a result of the popularity and size of the Ethereum blockchain, this standard has moved to other blockchains, allowing crypto assets to be used outside of Ethereum blockchain
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) – as one of the main advantages of the Ethereum platform, developers can use it to develop dApps
- Regular updates – due to Ethereum's open-source nature, the "whole world" participates in development
Weaknesses
- Programming language – Ethereum blockchain uses the Solidity and Vyper programming language, both novice and advanced developers may find them challenging
- Vulnerable ecosystem – Ethereum blockchain runs smart contracts that can be hacked or possess flaws
- High transaction fees – as a result of high network utilization, transaction fees can be high
- Regulation – in spite of the fact that the Ethereum blockchain is decentralized, it is heavily dependent on centralized servers that may one day be shut down by regulators or their operator
- Competition – Ethereum blockchain may have been the first to introduce smart contracts, however, in recent years several other blockchains have emerged that are striving to become better, and Ethereum is starting to fall behind
Basic Information
Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain that operates on Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus. The goal is to use blockchain more broadly, instead of just for Peer-2-Peer (P2P) transactions. Due to the support of Ethereum's dApps and smart contracts, we are able to see a wide range of applications that are based on Ethereum's decentralized systems.
The main unit of payment is the ether ($ETH), which is used to reward validators for managing the network. The smallest unit of $ETH is the wei.
Upgrade to premium
Functioning of the Chain
Despite some differences, Ethereum is similar to Bitcoin in many ways. Generally, the main difference between the two blockchains is their architecture. The Ethereum blocks contain a copy of the transaction list and the latest state. Furthermore, the block contains two additional values, the block number and the difficulty.
Ethereum's block verification algorithm is as follows:

It may seem that this solution is highly inefficient because it needs to store the entire state of the block with each subsequent block, but in reality it should have a similar efficiency to Bitcoin.
The state is stored in a tree structure, and after each block is finished, only a small part of the structure needs to be modified. Within two contiguous blocks, most of the trees should be identical. As a result, it is possible to store data once and use pointers (hashes of subtrees) to refer to it a second time. It is done using a special type of tree known as a "Petricia tree". It is modified by the Merkle tree concept, which allows efficient insertion and deletion of nodes rather than just changing them.
Since all information regarding the state is included in the last block, the entire blockchain history does not need to be stored.
The contract code verification process is part of the definition of the state transition function; specifically, the part of the algorithm for validating blocks. Therefore, if a transaction is added to block B, all nodes that download and validate the block will validate the code generated by the transaction.
By market capitalization, Ethereum is the number two blockchain in the world. Using the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus, it was only possible to process 15 to 30 transactions per second, which is a shockingly low rate. A heavy network load was hurting transaction prices. As a result of "The Merge" update, the Ethereum blockchain has been switched to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm, which is expected to accommodate 20 to 100 thousand transactions per second, rendering the network more efficient and more cost-effective.

Ethereum still needs to be tweaked in order to operate smoothly with cheap transaction fees. In 2023, the Ethereum blockchain is scheduled for a Shanghai upgrade, which hopes to further address the scaling issue.
In the past, Ethereum blockchains were ranked among the most expensive chains due to high transaction fees. It was intended that the Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP) 1559 would address the issue of high gas costs. However, it had little impact on the price of PoW consensus transactions.
Ethereum has operated on the PoW consensus since its launch in 2015. Soon after its launch, its transition to PoS was announced. The programming and testing have been ongoing for many years, and countless transition announcements have not been met. The Ethereum blockchain finally delivered on its long-standing promises on 15th September 2022 06:42:42 UTC in block #15 537 393. At that exact moment, the transition from PoW consensus to PoS was completed. Known as "The Merge", this upgrade ushered in a new era for Ethereum. It improved the sustainability of Ethereum's blockchain by reducing power consumption. The upgrade was also part of the Ethereum Foundation's ongoing upgrades which target improvements to scalability, security, and sustainability. The long wait and multi-year delay have unfortunately given time to competitors who have, in the interim, developed better sharding than Ethereum, one example of which would be NEAR blockchain.
Development History
2013
- the Ethereum blockchain whitepaper was published
2014
- at the Bitcoin conference, the launch of the Ethereum blockchain project was announced
- in the same year, Charles Hoskinson left the project due to disagreements within the team (he began working on his vision, which led to the development of the Cardano blockchain)
2015
- On June 30, Ethereum's mainnet was launched
2016
- The DAO raised 150 million USD in mass sales , a record at the time.
- In June, The DAO was hacked and 50 million USD worth of coins were stolen. This event has shaken the Ethereum community, which has split into two camps as a result. There were some that wanted to move on, while others wanted to "turn back the clock" and invalidate the coins that had been hacked in the past. It resulted in a network fork, which caused the original Ethereum to be renamed Ethereum Classic and remain in mining blocks. This newly created fork kept the Ethereum name and reversed the transactions as if no hack had occurred. However, other attacks against the Ethereum blockchain took place during the same year, which were also reversed by fork networks.
Since the Ethereum blockchain was launched in 2015, it has strived to move to a Proof of Stake consensus model. Therefore, the Difficulty Bomb was incorporated into the protocol to increase the difficulty of mining so that miners would find it very difficult to manage the Ethereum blockchain. The first deadlines for the transition to PoS were in 2017 and 2019. The deadlines were missed and the Difficulty Bomb got delayed as a result. To test PoS consensus and a variety of applications, the Beacon chain was launched for the first time in 2020.
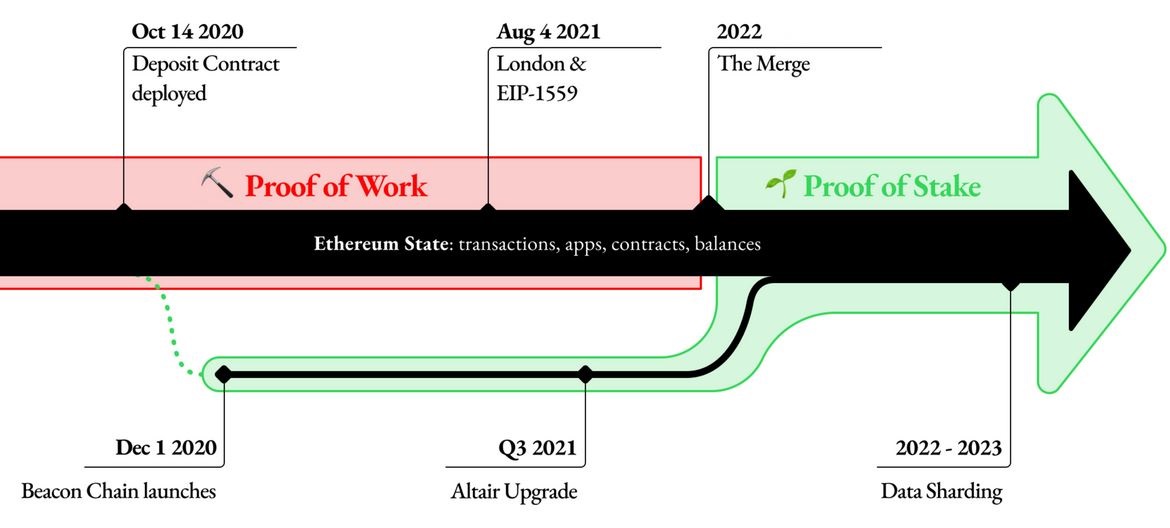
After many years of planning, things have started to take shape. Two years later, in 2022, Ethereum switched from a PoW to a PoS.
Every time "The Merge" has been delayed, the crypto community has mocked Ethereum and its supporters. According to them, it couldn't handle the switch to PoS. The Ethereum blockchain successfully switched to PoS in 2022. However, it continues to lag behind its competitors, who are miles ahead.
Team
The Ethereum blockchain has been and is being developed by many developers around the world. Here is a short list of some of them.

Other people involved in Ethereum blockchain development:
Ethereum has been operating for 7 years. Many people have contributed to its development over the years.
It is a large ecosystem that is constantly evolving and innovating. Therefore, new and fresh minds are required to ensure continuous innovation.
Governance
Ether ($ETH) is the main coin of the Ethereum blockchain.
Its use:
- a possibility to stake through your own node or by joining a liquid staking pool (LP)
- pays transaction fees on the Ethereum blockchain
Revenue & Tokenomics
$ETH does not have a limited supply.
New $ETH coins are created with each block.
$ETH ICO coin distribution:

The initial $ETH allocation looked like this:
- 16,7 % was allocated to the Ethereum Foundation and its initial investors
- 83,3 % was allocated to the Ethereum Crowdsale
$ETH supply schedule looked as follows:

Blue and red – show the initial ICO from 2014.
Yellow – rewards for mined PoW consensus blocks (taking into account the burning of a portion of the fees after the deployment of EIP 1559)
Green – rewards for validators after migration to PoS consensus
The total supply of $ETH coins as of November 23, 2022 is 120 516 450.
Due to the Merge, the issuance of new $ETH has been reduced by approximately 87 %. Previously, miners received 13 000 $ETH per day. As of today, new $ETH are issued in proportion to the total amount of $ETH that has been deposited in the staking pool. With 14 million $ETH deposited in the staking pool, 1700 $ETH are issued each day, thereby significantly reducing the number of new coins that enter circulation each day. As more $ETH is deposited in the staking, more will enter circulation.
Due to EIP 1559, there is a burn of a portion of the fees. With 14 million $ETH deposited in the staking pool, 1700 $ETH are issued each day. When the average value of a transaction payment over the course of 24 hours is 16 GWEI, we can say that the coins burned are in line with the coins issued. The $ETH is not an inflationary coin at this time.
Here's an informative page on the issuance and burning of $ETH.
The Uniqueness of the Chain
Ethereum forms a blockchain with a fully featured built-in programming language that can be used to create smart contracts. It is possible to code arbitrary functions using these, which allows users to create new decentralized systems.
How the Network is Secured
Network security is ensured by more than 472 thousand validators. They control the total amount of deposited $ETH in the staking pool - 15 135 584 coins.
There is still a threat of a 51 % attack on PoS; however, It is becoming increasingly difficult for attackers to do so.
It would be necessary for an attacker to control 51 % of the $ETH deposited in the staking in order to be able to use his own attestations to ensure that his block write is correct and accepted by a majority of the network. Based on the trustworthiness of the accumulated attestations, the correct chain is identified.
As a result, the attacker could create false entries in the ledger.
A strong characteristic of PoS is that the community has the flexibility to create counterattacks.
For instance, honest validators may decide to continue to create blocks on the "fake network" and ignore the unauthorized fork, while urging applications, exchanges, and funds to follow this lead. Alternatively, they may decide to remove the network forcibly, destroying the relevant $ETH. This is an effective economic defense against a 51 % attack.
Ethereum blockchain security is decentralized by a large number of validators. In order to participate in the network, they need a minimum of 32 $ETH. PoS consensus does not require as much computational power as PoW consensus, but even this small amount of power must be utilized somewhere. In most cases, these servers are leased through Google Cloud computing services or Amazon Web Services. The majority of the chain's power is provided by these services. Ethereum will have a difficult time if, in the future, these cloud services owned by large corporations are forced to ban validator nodes under the threat of government authorities.
Nodes
It is very easy to become a validator for the Ethereum blockchain. According to the $ETH stake options, validation can be divided into several categories:
Solo home staking:
This is the most ideal option. You retain complete control over your $ETH that is deposited in the stake and you receive the full reward.
It enhances the decentralization of the validation process.
Solo home staking sets up a node on the Ethereum blockchain that is connected to the internet. With a locking of 32 $ETH, the validator will be activated, allowing you to actively contribute to the security of the network.
Operating system:
All clients support major operating systems – Linux, MacOS, Windows.
Minimum requirements
CPU with 2+ cores
8 GB RAM
700 GB of free disk space
10+ Mbit/s bandwidth
Recommended specifications
Fast CPU with 4+ cores
16 GB+ RAM
Fast SSD with 1+ TB of free disk space
25+ Mbit/s bandwidth
The selection of a sync mode and client will have an impact on the amount of free disk space required. Here are the approximate free disk space requirements for each client:
Client Client disk size (synchronization) Disk size (full archive)
Geht 500 GB+ 12 TB+
Nethermind 500 GB+ 12 TB+
Besu 800 GB+ 12 TB+
Erigon N/A 2,5 TB+
Ethereum blockchain nodes consist of an Execution Client (EL) and a Consensus Client (CL). These clients are software that works in conjunction with a valid set of signature keys in order to verify transactions and blocks, collect attestations, and design blocks according to the specification.
Solo stake participants are responsible for maintaining the hardware necessary to run these clients. It is strongly recommended that you utilize a dedicated machine for this purpose, one that is free of interruptions and to which you have constant access.
Your client will then receive rewards directly from the protocol for working properly and being online. If the client were to go offline for any reason or at any time is prevented from verifying the chain, you risk losing portions of the staked $ETH or having your node removed from blockchain validation.
Staking as a Service (SaaS):
A SaaS service requires a minimum deposit of 32 $ETH to activate a node that is managed by a third party. Typically, this process involves performing the initial setup (generating the signature keys, storing them, and uploading them to the third party). As a result, the third party will be able to operate the node on your behalf.
The following are some services that specialize in this type of staking:
Key Generation App:
Staking pool:
Staking pools are suitable for users without sufficient $ETH to activate validation.
The Ethereum network does not support this feature, so it must be provided by individual applications.
Some funds utilize smart contracts to provide a trusted method of managing and tracking your deposits and issuing rewards. Other funds may not contain smart contracts and may instead be arranged off-chain.
The following apps support staking pools:
Keep in mind that if you deposit $ETH into staking, you cannot withdraw it.
Ethereum promised that this would be possible after the transition to PoS (The Merge).
As part of the Shanghai upgrade, they are planning to add the option to withdraw $ETH from the staking protocol.
The upgrade has been postponed several times since the switch to the PoS. Most recently, to mid-2023.
It is well known that Ethereum does not worry too much about pushing back deadlines.
Until then, your $ETH will be locked in the protocol, and you will not be able to manage it. Thus, you should carefully consider whether or not it is worth locking your $ETH, along with where and how you lock it up.
Road Map

Right now, Ethereum's biggest challenge is solving the sharding problem, which will reduce network load and increase the number of transactions per second. The first signs of implementation should be evident in 2023. One of the flagship upgrades will be the Shanghai upgrade, which will include the design of EIP 4844 and EIP 4895.
EIP 4844 will improve Ethereum's sharding.
EIP 4895 allows withdrawing $ETH coins from the staking pool.
Ecosystem
As the first blockchain with dApps and smart contracts, Ethereum is wildly popular with the community. Despite slow and expensive transactions, its DeFi world is the largest in terms of TVL.
The biggest projects on the Ethereum blockchain:
- MakerDAO – CDP
- Lido – Liquidity Staking
- AAVE – Lending platform
Over 500 projects are now part of the DeFi ecosystem.
The Total Value Locked (TVL) in DeFi on the Ethereum blockchain is 45,92 billion USD (November 22nd, 2022).
On its platform, Ethereum takes a responsible approach to development and offers a variety of tools to facilitate development. In order to support emerging projects on its platform, it has an extensive grant program.
Established projects with a large community also provide grants to emerging projects.
The Ethereum blockchain also has a Layer 2 (L2). The L2 blockchain is a separate blockchain that is just as secure as the Ethereum blockchain, but much faster and less costly. Everything that works on Ethereum (L1) will also work on L2. This is the reason why many dApps are migrating to L2.
Upon migration to PoS, it is anticipated that L2 will process transactions from L1. As a result, the Ethereum blockchain will become more efficient and cheaper.
L2 chain:
- Arbitrum
- Optimism
- Boba Network
- Polygon
An entire ecosystem is managed by the Ethereum Foundation. The Ethereum Foundation is an organization dedicated to the promotion of the Ethereum blockchain and related technologies.
Community
Ethereum’s Discord has a large number of administrators. They manage the smooth running of the channels and respond to questions.
They share news and interesting facts about the entire Ethereum ecosystem on Twitter.
They publish news that will be deployed on the blockchain on their YouTube channel.
Overall, the Ethereum blockchain community is very friendly and calm, even between different Ethereum projects. However, the greatest rivalry lies between the Ethereum and Bitcoin communities. No camp is willing to back down from its claim that its blockchain is superior.
For its users, Ethereum has created an Ethereum community hub featuring direct links to the most frequently requested topics
Partners
For its partners, Ethereum has created a separate project called the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance. With its help, companies can learn more about blockchain technology and get more involved in it.

Where to Buy
The purchase of $ETH is available on all centralized exchanges (CEX) and decentralized exchanges (DEX).
To purchase on a DEX, it is recommended to use those on the Ethereum blockchain:
- Uniswap
- Sushiswap
In the case of CEX, you are not limited by any exchange when purchasing. $ETH is the second-largest cryptocurrency, and almost all exchanges support it.
For example:
Supported Wallets
Ledger Nano X – the most commonly used hardware wallet (HW) on the market. Pairing it with your software wallet (SW) increases the security of your cryptocurrencies.
TrustWallet – SW wallet
MetaMask – SW wallet
Analyst Opinion
Ethereum is an improved version of Bitcoin, but it is still unable to become the top cryptocurrency. The transition from PoW to PoS, which was frequently joked about in the crypto community, has now become a reality. The PoS consensus should finally resolve Ethereum's long standing scaling issue in order to bring it at least a little closer to its competitors. Although competition has been on the scene for a shorter period of time, it is able to resolve the problem much more rapidly. It will be interesting to see everything unfold in a few months (maybe years) when the Bull Run comes and new and old users return to utilize the entire Ethereum ecosystem.
In terms of decentralization, I do not like PoS itself. Most of the network is hosted on leased servers, which may be shut down upon official request. I like the fact that it's less dependent on electricity. We will see whether it is more secure than PoW, which has a longer operating history.
My belief is that Ethereum, as the first blockchain supporting smart contracts and dApps, will prove that it has not rested on its laurels and will continue to compete with its competitors. It will enhance its chain with more upgrades that will increase its speed and reduce its fees. While there will always be other blockchains operating on the same consensus or a different one, Ethereum has the advantage of using its past history to attract new users.
Previous

Next






.webp)
.png)






.png)



.png)


.png)

.png)


.webp)


.png)


.png)


.png)




.png)
.png)


Social Networks
bitazza
wikipedia
ethereum.org
whitepaper