
Kava
Latest News
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
- Seamless scalability: fast and hassle-free thanks to the Tendermint core
- Incentives: attracts more talented developers into the ecosystem
- Co-chain: improves interoperability outside the Cosmos ecosystem
- CDP: receive a stablecoin for any collateral provided
- IBC: quick connection between other blockchains in the Cosmos ecosystem
Weaknesses
- Marketing: not well-known among the cryptocurrency community
- USDX stablecoin: experienced a de-peg in May 2022 to a price of 0.55 USD
Basic Information
The Kava blockchain combines the speed and interoperability of the Cosmos SDK with the flexibility and developer support of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), allowing the Ethereum and Cosmos chains to interact seamlessly with one another through Kava’s own co-chain infrastructure.
As part of the growing DeFi market, Kava distinguishes itself from other projects by being built on the Tendermint core, which adds some additional features.
Kava’s users can stake their cryptocurrencies and borrow loans in $USDX, Kava's stablecoin.
Similar to MakerDAO for the Ethereum blockchain, Kava provides several services, but with the expansive Cosmos ecosystem, it has a greater capacity for expanding DeFi services.
Upgrade to premium
Functioning of the Chain
The basis of Kava blockchain is:
- IBC (Inter Blockchain Communication) protocol
- Tendermint core
- Cosmos SDK (Software Development Kit)
The IBC protocol allows communication between two or more blockchain networks.
IBC is an internet protocol that communicates with and connects different servers, and entire blockchain networks. IBC enables the creation of an interchain account that will be the same across all blockchain networks that support IBC. This connection enables you to stake, trade, or participate in DeFi protocols across multiple blockchain networks from a single location.

All blockchain networks connected to IBC have a Tendermint core. Together with the Cosmos SDK, these are the building blocks of the network. With the same foundation, these blockchain networks can communicate easily, as the IBC takes data from one blockchain, wraps it, and unpacks it on the other blockchain in the correct format. This communication is possible despite different programming languages due to the same core being present throughout.
Kava addresses communication between the Ethereum blockchain and the Cosmos blockchain through its own two co-chains.

The two co-chains of the Kava blockchain function like two hemispheres of a single brain. The Cosmos co-chain is optimized for the developers of the Cosmos ecosystem, while the Ethereum co-chain is optimized for developers of the Ethereum ecosystem. The Translator module connects the two distinct execution environments of the co-chains, allowing them to seamlessly collaborate.
Ethereum co-chain: an EVM-compatible environment that allows dApps to utilize the scalability and security of the Kava blockchain.
Cosmos co-chain: a highly scalable and secure blockchain built on the CosmosSDK that connects the Kava blockchain with over 35 other chains in the Cosmos ecosystem through the IBC protocol.
As with all blockchains built on the CosmosSDK, certain modules have specific functions:
- Auction module: it is divided into three different types that correspond to specific functions
- Surplus auction: An auction in which a fixed lot of coins (c1) is sold for increasing amounts of other coins (c2). Bidders incrementally increase the amount of c2 they are willing to pay for the lot of c1. After the completion of a surplus auction, the winning bid of c2 is burned, and the bidder receives the lot of c1. As a concrete example, surplus auctions are used to sell a fixed amount of USDX stablecoins in exchange for increasing bids of KAVA governance tokens. The governance tokens are then burned and the winner receives $USDX
- Debt auction: an auction in which a fixed amount of coins (c1) is bid for a decreasing lot of other coins (c2). Bidders incrementally decrease the lot of c2 they are willing to receive for the fixed amount of c1. As a concrete example, debt auctions are used to raise a certain amount of USDX stablecoins in exchange for decreasing lots of KAVA governance tokens. The $USDX is used to recapitalize the CDP system and the winner receives $KAVA.
- Surplus Reverse auction: a two-phase auction in which a fixed lot of coins (c1) is sold for increasing amounts of other coins (c2). Bidders incrementally increase the amount of c2 until a specific maxBid is reached. Once this has occurred, a fixed amount of c2 is bid for a decreasing lot of c1. In the second phase, bidders incrementally decrease the lot of c1 they are willing to receive for a fixed amount of c2. As a concrete example, collateral auctions are used to sell collateral ($ATOM, for example) for up to a maxBid amount of $USDX. The USDX tokens are used to recapitalize the CDP system and the winner receives the specified lot of $ATOM. In the event that the winning lot is smaller than the total lot, the excess $ATOM is ratably returned to the original owners of the liquidated CDPs that were collateralized with that $ATOM.
- BEP3 module: implements the BEP3 protocol for secure transfers of assets between the Kava blockchain and other BEP3-compatible chains, such as the BNB Chain.
- Collateralized Debt Position (CDP) module: allows for the creation of a stable asset by collateralizing it with another asset on the blockchain. The stable asset can thus be freely transferred among users, but the CDP owner must repay their debt to regain their collateral.

- Committee module: provides a supplementary management function to the x/gov module by allowing the creation of committees or groups of addresses that can vote on proposals they have permission for, bypassing the usual management structures in the chain
- Hard module: manages and provides functionality for the two-way money market protocol with autonomous interest rates. The main state transitions in the hard module consist of deposit, withdrawal, loan, and repay actions.
- Incentive module: implements incentives for users that are governed by management. When users perform a certain action, such as opening a CDP, they become eligible for a reward. Rewards are opt-in, meaning users must send a message before the deadline to claim the reward.
- Issuance module: enables the issuance of assets into the Kava blockchain. The issuer of assets has the exclusive right to decide on the buyback (burn) of the asset, or to restrict access to the asset by confiscating it.
- Kava Dist module: designed to determine the correct inflationary period and APR inflation rate for each period. The module mints coins on each block according to the schedule. Governance can change the APR by submitting a proposal to change parameters.
- Pricefeed module: an oracle that determines and publicly announces prices with every block
- Swap module: manages and provides functionality for the Auto Market Maker (AMM) protocol. The main state transitions in the swap module include deposits / withdrawals into liquidity pools by liquidity providers, and token swaps performed against liquidity pools by users.
Kava Mint
Kava Lend
Kava Swap
CDP isresponsible for issuing the USDX stablecoin, which is the native stablecoin inthe Kava ecosystem. You can obtain $USDX in the Mint part of the protocol byusing your cryptoassets as collateral. You can borrow up to 67 % of the valueof your cryptoassets in $USDX. Its stability is derived from market flows,which are influenced by Kava governance. Kava has introduced several measuresto return $USDX to a value close to 1 USD, but unfortunately, it has not yetsucceeded. It could be said that this model works until it doesn't.

Development History
2019
- Kava blockchain developed and launched by Kava Labs
- Public token sale on Binance exchange
2020
- June: Kava’s 3rd launch, supporting Kava Lending Platform and collateral types $BNB, $BTC, $BUSD and $XRP
- October: 4th upgrade launches, supporting HARD protocol
2021
- March: 5th "Gateway" upgrade launches, supporting version 2 of HARD protocol
- June: 6th upgrade launches, releases AMM service and application, Kava SAFU fund, and Kava staking derivatives
- July: 7th upgrade launches, releases Robo Advisor service and application, and launches Ethereum bridge to Kava
- August: 8th upgrade launches, launches direct bridge from Bitcoin to Kava
- December: Development of co-chain for Ethereum blockchain begins
2022
- January: Kava’s 9th upgrade launches, brings IBC integration
- May: 10th upgrade launches, bringing co-chain architecture and connecting Cosmos and Ethereum blockchain
- June: Ethereum co-chain launches
- October: 11th upgrade launches, bringing liquidity staking and launching the Kava Rise program
2023
- February 15th: the latest Kava’s 12th upgrade launches, enhancing key Dao functions and emission management
The Kava blockchain is very fast and its connection of Ethereum and Cosmos users is well executed. The website is clear and everything is intuitive. If you are just looking for staking, or you don't want to sell your assets and just borrow against them, you are in the right place. Regular updates every few months always bring new features or security patches, which will give you even more confidence in this blockchain.
Team
The Kava blockchain is run by the Kava Labs team:
- Brian Kerr - Co-founder and CEO of Kava labs
- Scott Stuart - Co-founder and Head of Product
- Ruaridh O'Donnell - Co-founder and Lead Developer
- Kevin Davis - Lead Engineer
- Terry Chen - COO
- Aaron Choi - VP of Global BD of Kava (Asia)
The Kava Labs team is very active and aims to regularly bring updates and improvements to their blockchain, but unfortunately, they have a tendency not to deliver these updates on time, with delays on a regular basis. This may be due to a lack of willingness or resources on the team's part, but it is important to keep in mind that some promises may not always be fulfilled in a timely manner. Therefore, users should remain patient and understand that the team is doing their best to make improvements, even if they may take longer than expected.
Brian Kerr: An entrepreneur who was involved in theestablishment and growth of the Fnatic esports organization. He is also anenthusiastic cryptocurrency investor and advisor to several crypto projects(Akash, Frontier, and Snowball.money).
RuaridhO'Donnell: A software developer with experience inresearch and innovation. He previously worked at AppEase on machine learningdevelopment and worked on systems for data analysis and fraud detection.Ruaridh graduated from the University of Glasgow with a master's degree inphysics.
Governance
KAVA is thegovernance coin for the Kava blockchain.
Its uses include:
- Staking
- Voting
- Validator rewards
- Incentives
Anyone with 1000$KAVA can propose a change to the Kava blockchain. You can vote using yourstaked KAVA coins with a validator. If you have a larger number of staked coinsthan your validator, your vote has a higher priority. If you do not vote, yourvalidator will vote instead of you.
Governance on theKava blockchain may appear less decentralized. The largest validator has 13.3 %of the total staked coins (20. January 2023) and the top 10 validators have acombined 65 % of the staked coins. It is important to note that the totalnumber of staked KAVA coins is 102 million, while 100 million more areavailable (as of 31 January 2023). Approval of a proposal requiresapproximately 50 million votes.
Revenue & Tokenomics
Revenue
Kava has secured funding through private sales and an Initial Offerings of Exchange (IOE) on the Binance exchange, where 6.52 million USD was raised. In subsequent funding rounds, the Kava blockchain raised a further 1.2 million USD.
Revenue is generated from fees for using the Kava blockchain, which is then used to fund and develop the project. These fees can come from transactions within the platform, such as loans or staking of the KAVA coin. The estimated revenue for 2022 was around 6 million USD, which was spent on employee payouts and the operations of the Kava Foundation.
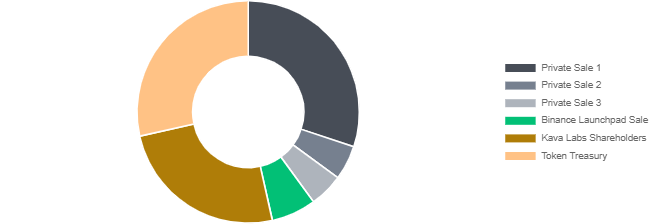
The distribution of $KAVA will be as follows:
- Private sale 1 - 30.05 % of total supply
- Token treasury - 28.48 % of total supply
- Kava Labs shareholders - 25 % of total supply
- Binance launchpad sale - 6.52 % of total supply
- Private sale 2 - 5.02 % of total supply
- Private sale 3 - 4.93 % of total supply
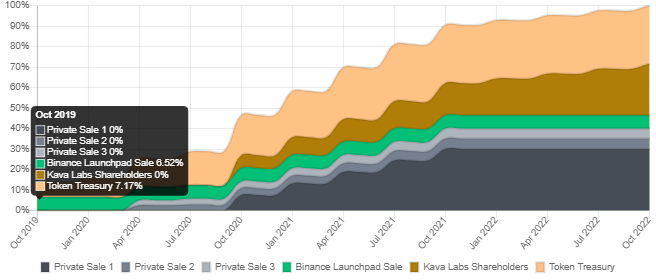
The release of $KAVA into circulation is ongoing, with newly created coins being distributed to validators and delegates. The number of newly created KAVA coins is variable and depends on the overall percentage of $KAVA being staked.
The target inflation rate for the KAVA coin is set so that 2/3 of the total supply is staked. This mechanism is intended to motivate users to stake and participate in the network's operations.
The total inflation is set at 7 %. If the staked $KAVA coins amount is less than 2/3 of the total supply, the block rewards will increase to up to 20 % of the total annual supply. If more than 2/3 of the total supply is staked, the rewards for each new block can be reduced to 3 % annual inflation.
The coin emission for each new block looks like this:

Most of the new coins go to incentives for developers in the Kava Rise program, and the rest to validators as rewards.
Total supply:

As of 31 January 2023, the total supply of $KAVA is 395,483,679 coins.
Of these, 102,128,146 coins (approximately 26 %) are delegated to validators.
The Uniqueness of the Chain
Cosmos co-chain
Kava was built on the Cosmos SDK and through integration with the Cosmos co-chain, it connects the Kava blockchain with the Cosmos ecosystem.
Ethereum co-chain
The Ethereum co-chain provides an effective connection between Kava and Ethereum blockchains. Thanks to compatibility with the EVM, Ethereum dApps can run on this platform. This means that the co-chain allows developers to write code for dApps using the Ethereum EVM programming language (Solidity). When these codes are written, the EVM can compile them, even when running on the Kava platform. EVM compatible dApps can then benefit from the scalability of the Kava blockchain.
Kava fully leverages its potential as a lending protocol in the Cosmos ecosystem. Thanks to a feature of the Cosmos system known as zones, users of the Kava lending protocol can deposit a wide range of foreign cryptocurrencies, such as $BNB, $BTC, $ETH, and other significant cryptocurrencies. In the future, more options for collateralizing different cryptocurrencies for $USDX will be introduced, which users will be able to borrow in the Cosmos ecosystem.
How the Network is Secured
The security of the Kava blockchain is monitored by 100 validators. Kava uses the slashing function to oversee the proper functioning of validators and to deter fraudulent behavior. If fraud is proven, the slashing function burns a portion of the validator's staked assets, based on the severity of the fraud.
- Inactive: a validator is considered inactive if they do not participate in consensus for more than 28,500 blocks in a row (approximately 48 hours). The validator is then jailed and removed from the active set. They can send a transaction to unlock themselves (confirming their activity) and rejoin the validation.
- Double-signing of blocks: this is highly harmful to the chain, and such behavior is penalized. If double-signing is proven, 5 % of the validator's total staked deposit will be burned, and they will be permanently removed from the active set of validators (becoming a so-called "graveyard").
When selecting a validator, be careful to choose an honest one, or you may lose some of your assets. If a validator is removed from the active set, all their delegated coins are returned to the original wallets.
The security of the Kava blockchain is the main priority, so an audit was conducted on major contracts to ensure their safety by the company Certik.
Kava does not have an official Bug Bounty program. If you find a bug in the protocol or any other vulnerability, you can report it to this email security@kava.io or by filling in the form on the website.
Interchain security: this is a solution to the security problem for new blockchains that will allow validators of larger blockchain networks to provide security for small blockchain networks. After interchain security is introduced, validators for the Kava blockchain will no longer be necessary. All security will be provided by Cosmos Hub.
Nodes
Own Node:
To run a node on the Kava blockchain, the minimum hardware requirements are:
- 4 core CPU
- 8 GB RAM
- 5 GB per month
Then, visit this site, which will guide you through a detailed setup of the node.
After setting up and launching a validator node, you can check the list of all Kava blockchain validators at here, where your validator node will also be listed.
Benefits of own node:
- Delegate rewards distribution
- Delegate fee for enabling staking
- Contribution to network security
Delegate:
If you don't want to run your own node, you can delegate your coins to an existing validator through your wallet that supports the Kava blockchain.
- Connect your wallet to the Kava blockchain
- Click "Stake"
- Select a validator
- Click ”Manage"
- Select the amount of KAVA coins
- Click "Delegate"
Advantages of being a delegate:
- No hardware needed
- Easy setup
- Contributing to the running and security of the blockchain
- Rewards from validators
When choosing a validator, only choose an active one or you won't receive any rewards, because the validator will not participate in validating the chain.
You can also stake your $KAVA on a centralized exchange (CEX). Here is a list.
Road Map
The Road Map for 2023 is in preparation.
The latest 12th update, which is set to arrive on 15 February 2023, will include the main upgrade of a new Kava Mint module, which will bring greater DAO control over reward distribution.

Ecosystem
The Kava blockchain has a large DeFi world with over 50 protocols. Here are the 3 largest:
- Kava Mint - CDP
- Kava Lend - Lending
- Kava Earn - Yield aggregator
The Kava blockchain has a program to support new and existing developers, called Kava Rise. The program will reward the best projects and their developers on Ethereum and Cosmos co-chains in the Kava blockchain, distributing 200 million KAVA coins over 4 years. Incentives will be given transparently on chain, based on the utilization of each protocol.
Community
Discord is the main communication portal for the Kava blockchain. It is not the largest community but it is pleasant and communicative. Any problem or question will be quickly resolved.
Information about what’s happening on the blockchain is updated daily on Twitter, including new updates, delays, new collaborations, or the listing of the $KAVA on new exchanges.
There are only 5 videos on Kava’s YouTube channel, which are one year old. These tutorial videos will help you orient yourself on the Kava blockchain and understand its basic functioning.
Partners
Investors:

Other investors in the Kava blockchain include:
- Binance labs
- Arrington XRP Capital
- SNZ Co. Ltd.
- Framework Ventures
- Xpring
Partners:
Kava's largest blockchain partners include:
- Certik
- cBridge
- Huobi
- Chainlink
- Swipe
Where to Buy
KAVA coin can be bought on almost all centralized exchanges (CEXs) that operate in the crypto world.
To buy on a decentralized exchange (DEX), use one directly through the Kava blockchain:
When buying on a CEX, always check if it supports K$AVA. The KAVA coin is the 104th largest cryptocurrency and is therefore supported by almost all CEXs.
For example:
Supported Wallets
Ledger Nano X - the most popular hardware wallet (HW) on the market. By pairing with your software wallet (SW), you will gain greater security for your cryptocurrencies
Trust Wallet - SW wallet
Keplr Wallet - SW wallet
Analyst Opinion
Kava blockchain and its co-chain infrastructure are an interesting alternative for Ethereum or Cosmos blockchains users who want to try something new. One of the main advantages is the speed and low fees when conducting transactions. The co-chains allows users to use their existing Ethereum or Cosmos blockchains, which is great for those who don't want to fully switch to a new platform.
However, in the DeFi space, Kava is still in its early stages of development. It supports several currencies that can be used as collateral to obtain $USDX, but this stablecoin has problems maintaining its value, so you should be aware of the risk before using it. On the other hand, staking $USDT, $BNB, $USDC, or $KAVA can be done directly in Kava Earn and gain you a decent percentage.
The Kava development team strives to bring regular updates and improvements to the platform. Unfortunately, these updates are not always timely, and are often delayed by a few days or weeks. This could either be due to reluctance or a lack of capacity within the team, so it's important to keep in mind that some promises may not always be fulfilled on time.
Previous

Next





.webp)
.png)






.png)



.png)


.png)

.png)


.webp)

.png)


.png)


.png)




.png)
.png)
.png)


Social Networks
Currency
Medium
Bybit learn
App Kava
Official web
Youtube
Atomicwallet
Kava Doc
Coingecko
Defillama
Medium Kava netwrok