Dexible
Opportunities & Risks
Introduction
Dexible allows trading cryptocurrencies in a decentralized environment and offers traders several necessary trading orders such as limit orders, stop limit orders, take profit orders, trailing stop orders, segmented market orders, stop loss orders, and TWAP orders. The Dexible platform is becoming more and more familiar to retail and institutional traders. In this article, we will go through some of the trading strategies offered by the Dexible platform.
Upgrade to premium
Types of Strategies for Investing into a Protocol and Risks

On Dexible, traders can choose from several order types. To choose a specific order, you need to decide which one best suits your strategy and will ensure a profit or protect your capital.

TWAP: Using the TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price) order, traders can enter or exit new positions sequentially and get an average price over a period of time. Only part of the order can be activated during a dip or peak. If traders use the "Price Bounds" feature they can set upper or lower price limit conditions independently. They can also set a time period using "Time Period" during which TWAP orders will be executed, where small values are bought at the average or lower price with breaks until the set period expires.
This strategy can be used by traders who do not want to enter a position with one large order but want to divide it into several entries to get an average price. The platform, if you use it in the recommended settings, will calculate the number of ideal entries by itself and show you everything in the platform interface. You can also customize your order separately by clicking on "Customization" where you will be able to set the Number of Swaps, Gas Strategy, Order Expiration, and Order Slippage.
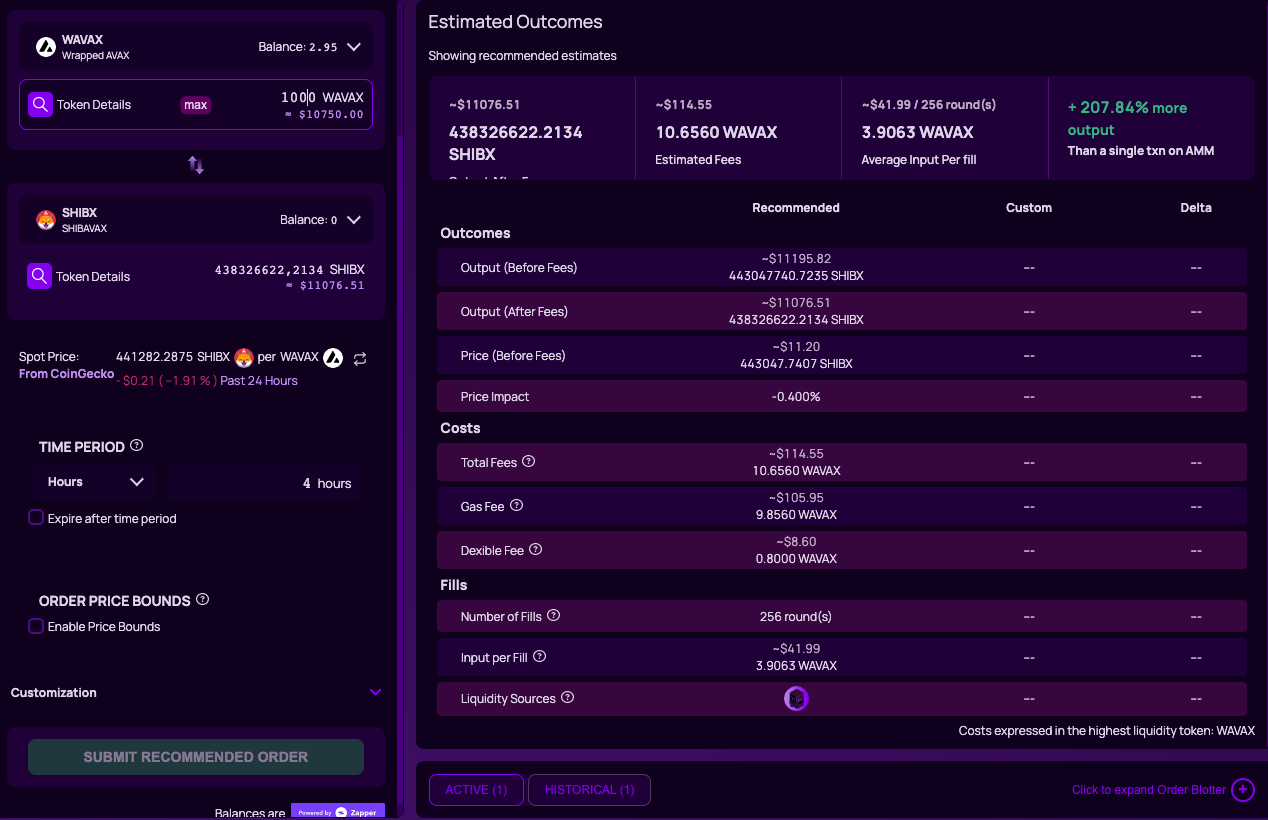
Segmented Order: To simplify the swapping of larger amounts of capital in an illiquid market, traders use a segmented order. Segmented orders are designed to minimize problems such as slippage and price impact, which are very common in an illiquid environment. Solving the problem of slippage and price impact is achieved by splitting orders into multiple smaller rounds over a period of time, allowing them to draw on many sources of liquidity while providing room to stabilize with other orders. When using this type of order, large orders can appear practically invisible.
The strategy is suitable for traders looking to swap larger amounts of capital while having the least amount of slippage and price impact.
Limit: With limit orders, traders can buy or sell assets at a set (limit) or better price. By entering a limit order, an input asset is exchanged for an output asset when the price of the output asset exceeds the price of the input asset.
The limit strategy is suitable for traders who have determined by analysis at what prices it is acceptable for them to buy a chosen asset. By setting a limit order, they can get it at a better price. The algorithms will do the buying for them once this price is reached.
Stop Loss: Stop loss is used by traders to preserve capital or protect profits during a price drop in the market. Stop loss orders have a trigger price at which the market order is executed.
The strategy is used by traders to protect their capital in the case that an asset falls below a value that is no longer acceptable to them. At the level set by them, algorithms take care of the exchange of the selected assets.
Stop Limit: When traders want to execute a limit order in a specific price range, they use a stop limit order. A stop limit order waits until market prices reach a certain price at or above the trigger price before it becomes a limit order. The trader sets the trigger price and limit price themselves in the platform interface. The specified limit price acts as the maximum price at which he is willing to execute an exchange. The limit order is executed when the token price reaches the stopping point set by the trader.
The strategy serves more experienced traders who can analyze well the appropriate price ranges at which they are willing to exchange assets.
Trailing Stop: Traders use a trailing stop order when an asset is rising so that if the market reverses, they can maintain their profits at their set percentage of the peak price. The trailing stop serves to protect profits by allowing the trade to remain open and continue to yield a profit as long as the price moves in the investor's direction. The order closes the trade if the price changes direction by a percentage set by the trader in the Dexible platform interface from the peak price.
The strategy works similarly to a stop loss, but with the difference that its value is set in the percentage interface from the peak where the price turns. With the trailing stop strategy, traders can multiply their profits when the price of the asset is still going in their direction and only lose a set percentage, where the trade is closed and they keep most of their profits.
Take Profit: The take profit order is used by traders to secure profits and avoid capital losses. A take profit order is triggered when a set percentage price threshold is crossed, which initiates a limit order that behaves like a reverse stop loss order, designed to swap assets to secure profits. Take profit works based on two price conditions, similar to a stop limit order. When the price reaches the desired trigger price, it automatically sends a limit order to secure unrealized gains.
The Take Profit strategy will automatically ensure traders make a profit if the asset reaches the value set by them (On Dexible, these values can only be set as a percentage). Take profit orders are particularly beneficial for short-term traders who are interested in taking profits from a quick rise in the price of an asset.
History of Similar Protocols
DEX protocols that offer features like Dexible in the form of limit orders are DydX (Ethereum), GMX (Arbitrum, Avalanche), Kwenta (Optimism) and Spin (Near). The mentioned protocols also offer leveraged trading compared to Dexible. DEX protocol with limit orders which are much needed for cryptocurrency trading attracting more and more traders from CeFi to DeFi. After the collapse of FTX, DEXs with these features started to gain even more traction and are doing very well. There is healthy competition that is forcing developers to constantly work on improving their apps to offer traders the best user interface possible.
Conclusion
We have mentioned the specific opportunities and strategies we use to trade on the Dexible platform. The functionality and individual orders may remind you of trading on CEX, except that on Dexible you don't have to give out your personal information to anyone. If you are interested in a more detailed analysis, detailed functioning, and security of the platform, please read Dexible - Protocol. If you want to start trading on Dexible, familiarize yourself thoroughly with each strategy first and always start with a small amount of capital to lose. By taking a sensible and responsible approach, you can make consistent profits through the Dexible app.
Analyst
René Užovič



.webp)



